Data model
GDPR view
The GDPR view contains all the data required to maintain the data processing register, and provides a link with the processes, applications, and information used by the information system.
This view is used to fulfill the obligations set out in article 30 of the GDPR.
Register
The register of processing activities contains the information required by article 30.1 of the GDPR.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| data_processing | /api/data-processings |
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | Processing name |
| description | longtext | Processing description |
| legal_basis | varchar(255) | Legal basis for processing |
| responsible | longtext | Responsible person for processing |
| purpose | longtext | Purposes of processing |
| lawfulness | text | Legality of processing |
| lawfulness_consent | tinyint(1) | Legality based on consent |
| lawfulness_contract | tinyint(1) | Contractual legality |
| lawfulness_legal_obligation | tinyint(1) | Legality based on legal obligation |
| lawfulness_vital_interest | tinyint(1) | Legality based on vital interest |
| lawfulness_public_interest | tinyint(1) | Legality based on public interest |
| lawfulness_legitimate_interest | tinyint(1) | Legality based on legitimate interest |
| categories | longtext | Categories of recipients |
| recipients | longtext | Data recipients |
| transfer | longtext | Data transfers |
| retention | longtext | Retention periods |
| controls | longtext | Security Measures |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
The field "controls" is not used and therefore is absent in the app.
The data model export lists processes, information, applications and documents linked to a data processing.
In the app, a process can be linked to a data processing from a data processing object.
An information can be linked with a data processing from a data processing object.
An application can be linked to a data processing from a data processing object.
A document can be linked to a data processing from a data processing object.
Security measures
This table identifies the security measures applied to processes and applications.
By default, this table is populated with the security measures of ISO 27001:2022.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| security_controls | /api/security-controls |
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | measure name |
| description | longtext | measure description |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
Ecosystem view
The ecosystem view describes all the entities or systems that revolve around the information system considered in the mapping.
This view not only delimits the scope of the mapping, but also provides an overall view of the ecosystem without being limited to the individual study of each entity.
Entities
Entities are a part of the organization (e.g.: subsidiary, department, etc.) or related to the information system to be mapped.
Entities are departments, suppliers, partners with whom information is exchanged through relationships.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| entities | /api/entities |
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | Unique identifier of the entity |
| name | varchar(255) | Name of entity |
| icon_id | int unsigned | Reference to a specific image |
| entity_type | varchar(255) | Type of entity |
| attributes | varchar(255) | Attributes (#tag...) |
| description | longtext | Entity description |
| reference | varchar(255) | Reference the billing number of the entity |
| parent_entity_id | int unsigned | Pointer to the parent entity |
| is_external | boolean | External entity |
| security_level | longtext | Security level |
| contact_point | longtext | Contact point |
| external_ref_id | varchar(255) | Link to connected external entities |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
The "external_ref_id" field is not used and therefore is missing in the app.
The data model export lists processes and applications linked with an entity.
In the app, a process can be linked with an entity from these two objects.
An application can be linked with an entity (as operations manager) from these two objects.
In the app, a database can be linked with an entity (as operations manager) from these two objects.
Relationships
Relationships represent a link between two entities or systems.
Relationships are contracts, service agreements, legal obligations... that have an influence on the information system.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| relations | /api/relations |
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | Relationship name |
| type | varchar(255) | Type of relationship |
| attributes | varchar(255) | Attributes / #tags of the relationship |
| description | longtext | Description of relationship |
| source_id | int unsigned | Reference to source entity |
| destination_id | int unsigned | Reference to destination entity |
| reference | varchar(255) | Reference number of the relation (billing) |
| responsible | varchar(255) | Responsible of the relation |
| order_number | varchar(255) | Ordre number (billing) |
| active | tinyint(1) | Is the reation still active |
| start_date | date | Start date of the relation |
| end_date | date | End date of the relation |
| comments | text | Comment on the status of the relation |
| importance | int | Importance of relationship |
| security_need_c | int | Confidentiality level needed |
| security_need_i | int | Integrity level needed |
| security_need_a | int | Available level needed |
| security_need_t | int | Traceability level needed |
| security_need_auth | int | Authenticity level needed |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
In the app, the field for the authenticity need ("security_need_auth") is hidden by default. It is mandatory for
entities subject to the regulation (EU) 2022/2554 (DORA).
This default configuration can be changed in the menu Configuration > Parameters.
The data model export lists the reference documents attached to a relationship.
In the application, a document can be attached to a relationship from a relationships object.
The financial values of a contract can be indicated in dedicated fields.
Business view of the information system
The business view of the information system describes all the organization's business processes and the players involved, independently of the technological choices made by the organization and the resources made available to it.
The business view is essential, as it allows you to reposition technical elements in their business environment, and thus understand their context of use.
Macro-processes
Macro-processes represent sets of processes.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| macro-processuses | /api/macro-processuses |
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | Name of macro process |
| description | longtext | Description of macro-process |
| io_elements | longtext | Incoming and outgoing elements |
| security_need_c | int | Confidentiality |
| security_need_i | int | Integrity |
| security_need_a | int | Availability |
| security_need_t | int | Traceability |
| security_need_auth | int | Authenticity |
| owner | varchar(255) | Owner |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
In the app, the field for the authenticity need ("security_need_auth") is hidden by default. It is mandatory for
entities subject to the regulation (EU) 2022/2554 (DORA).
This default configuration can be changed in the menu Configuration > Parameters.
In the application, a process can be linked with a macro-process from these two objects.
Processes
Processes are a set of activities designed to achieve a goal. The process produces value-added information ( output) (in the form of deliverables) from information (input) produced by other processes.
Processes are made up of activities, entities involved in this process, and information processed by this process.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| processes | /api/processes |
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | Process name |
| description | longtext | Process description |
| icon_id | int unsigned | Reference to a specific image |
| owner | varchar(255) | Process owner |
| in_out | longtext | incoming and outgoing elements |
| security_need_c | int | Confidentiality |
| security_need_i | int | Integrity |
| security_need_a | int | Availability |
| security_need_t | int | Traceability |
| security_need_auth | int | Authenticity |
| macroprocess_id | int unsigned | Reference to macro-process |
| activities | List int [,] | IDs list of related activities |
| entities | List int [,] | IDs list of related entities |
| informations | List int [,] | IDs list of related information |
| applications | List int [,] | IDs list of related applications |
| operations | List int [,] | IDs list of related operations |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
In the app, the field for the authenticity need ("security_need_auth") is hidden by default. It is mandatory for
entities subject to the regulation (EU) 2022/2554 (DORA).
This default configuration can be changed in the menu Configuration > Parameters.
The data model export lists:
- entities,
- activities,
- information,
- applications,
- data processing,
- and security measures
linked to a process.
In the application, an entity associated with a process can be linked with a process from these two objects.
An activity can be linked with a process from these two objects.
An information can be linked with a process from these two objects.
An application can be linked with a process from these two objects.
A GDPR registry data processing can be linked with a process from a registry data processing object.
A security measure can be linked with an application from the "Assign security controls" button.
This button is in the GDPR view and visible in the list of Security controls objects.
Activities
An activity is a step required to carry out a process. It corresponds to a specific know-how and not necessarily to an organizational structure of the company.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| activities | /api/activities |
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | activity name |
| description | longtext | Activity description |
| recovery_time_objective | int signed | RTO, Recovery Time Objective |
| maximum_tolerable_downtime | int signed | Maximum tolerable downtime |
| recovery_point_objective | int signed | RPO, Recovery Point Objective |
| maximum_tolerable_data_loss | int signed | Maximum tolerable Data Loss |
| drp | text | Description of the disaster recovery plan (DRP) |
| drp_link | varchar(255) | Link (URL) to the DRP |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
The maximum tolerable downtime is the limit after which the downtime effets are critical or unacceptable.
The maximum tolerable data loss is the limit after which the data loss is critical or unacceptable.
The data model export lists processes, operations, and applications linked with an activity.
In the app, a process can be linked with an activity from these two objects.
An operation can be linked with an activity from these two objects.
An application can be linked with an activity from these two objects.
In the app, the "Impact Type" and "Severity" fields are managed in a separate table.
Impacts
Impacts are the consequences of the occurrence of a risk during an activity.
Impacts are only accessible through "activities" objects.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| activity_impacts | N/A |
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | bigint signed | auto_increment |
| activity_id | int unsigned | Link to the activity related to this impact |
| impact_type | varchar(255) | Kind of impact (finance, brand, environnement, other...) |
| severity | tinyint(4) | Impact description |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| Champ | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | bigint signed | auto_increment |
| activity_id | int unsigned | Link to the activity related to this impact |
| impact_type | varchar(255) | Kind of impact (finance, brand, environnement, other...) |
| severity | tinyint(4) | Impact description |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
Operations
An operation is made up of actors and tasks.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| operations | /api/operations |
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | Name of operation |
| description | longtext | Description of operation |
| process_id | int unsigned | Reference to the process of which the operation is part |
| actors | List int [,] | IDs list of related actors |
| tasks | List int [,] | IDs list of related tasks |
| activities | List int [,] | IDs list of related activities |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
The data model export lists activities, actors, and tasks linked to an operation.
In the app, an activity can be linked with an operation from these two objects.
An actor can be linked to an operation from the object "operation".
A task can be linked to an operation from the object "operation".
Tasks
A task is an elementary activity performed by an organizational function and constituting an indivisible unit of work in the value-added chain of a process.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| tasks | /api/tasks |
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | Task name |
| description | longtext | Task description |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
The data model export lists operations linked to a task.
In the app, an operation can be linked to a task from the object "operation".
Actors
An actor is a representative of a business role who performs operations, uses applications, and makes decisions within processes. This role can be carried by a person, a group of people, or an entity.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| actors | /api/actors |
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | actor's name |
| nature | varchar(255) | Nature of actor |
| type | varchar(255) | Type of actor |
| contact | varchar(255) | Actor contact |
| operations | List int [,] | IDs list of related operations |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
The data model export lists operations linked with an actor.
In the app, an operation can be linked with an actor from the object "operation".
Information
Information is data processed by a computer.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| information | /api/information |
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | Name of information |
| description | longtext | Description of information |
| owner | varchar(255) | Owner of information |
| administrator | varchar(255) | Information administrator |
| sensitivity | varchar(255) | Sensitivity of information |
| storage | varchar(255) | Information storage |
| security_need_c | int | Confidentiality |
| security_need_i | int | Integrity |
| security_need_a | int | Availability |
| security_need_t | int | Traceability |
| security_need_auth | int | Authenticity |
| constraints | longtext | Legal and regulatory constraints |
| retention | varchar(255) | Information retention period |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
The field "retention" is not used and therefore is absent in the app.
In the app, the field for the authenticity need ("security_need_auth") is hidden by default. It is mandatory for
entities subject to the regulation (EU) 2022/2554 (DORA).
This default configuration can be changed in the menu Configuration > Parameters.
The data model export lists databases and processes linked with information.
In the app, a database can be linked with an information from the object "database".
A process can be linked to an information from these two objects.
Applications view
The application view is used to describe part of what is classically referred to as the "computer system".
This view describes the technological solutions that support business processes, mainly applications.
Applications blocks
An application block represents a set of applications.
An application block can be: office applications, management applications, analysis applications, development applications, etc.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| application-blocks | /api/application-blocks |
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | Name of information |
| description | longtext | Description of application block |
| responsible | varchar(255) | Responsible for application block |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
In the app, an application can be linked to an application block from these two objects.
Applications
An application is a coherent set of IT objects (executables, programs, data, etc.). It is a grouping of application services.
An application can be deployed on one or more logical servers.
When there is no virtualized environment, there are not several logical servers per physical server, but one logical server per physical server.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| m_applications | /api/applications |
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | Name of the application |
| application_block_id | int unsigned | Group of application |
| attributes | varchar(255) | Attributes of the application |
| description | longtext | Description |
| icon_id | int unsigned | Reference to a specific image |
| responsible | varchar(255) | Person/team responsible |
| functional_referent | varchar(255) | Functional referent |
| editor | varchar(255) | Application's editor |
| users | varchar(255) | Number of users and type |
| technology | varchar(255) | Technology |
| type | varchar(255) | Type of application |
| external | varchar(255) | External |
| install_date | datetime | Date of installation |
| update_date | datetime | Date of upgrade |
| next_update | datetime | Date of next planned upgrade |
| documentation | varchar(255) | Link to documentation |
| security_need_c | int | Confidentiality |
| security_need_i | int | Integrity |
| security_need_a | int | Availability |
| security_need_t | int | Traceability |
| ecurity_need_auth | int | authentication |
| rto | int | Recovery Time Objective |
| rpo | int | Recovery Point Objective |
| vendor | varchar(255) | Application's vendor |
| product | varchar(255) | Product name |
| version | varchar(255) | Version of the application |
| patching_frequency | int | Patching frequency |
| entities | List int [,] | IDs list of related entities |
| processes | List int [,] | IDs list of related processes |
| services | List int [,] | IDs list of related services |
| databases | List int [,] | IDs list of related dataabses |
| logical_servers | List int [,] | IDs list of related logical_servers |
| activities | List int [,] | IDs list of related activities |
| containers | List int [,] | IDs list of related containers |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
RTO : Recovery Time Objective
RPO : Recovery Point Objective
The "patching_frequency" and "next_update" fields are not used at the moment and are therefore missing from the application.
In the app, the need for authentication is hidden by default. It is mandatory in the case
from an entity subject to EU Directive 2022/2554 (DORA).
It is activated from the Configuration > Settings menu.
Export of reference data model:
- user entities (entities field),
- supported processes,
- supported activities,
- application services,
- databases,
- workstations,
- logical servers,
- logical security devices,
- administrators ("Users" object of the administration view),
- and security measures
linked with an application.
In the app, an entity using the application can be linked with an application from an application object.
A process can be linked with an application from these two objects.
An activity can be linked with an application from these two objects.
An application service can be linked with an application from these two objects.
A database can be linked to an application from these two objects.
A workstation can be linked to an application from a workstation object.
A logical server can be linked with an application from these two objects.
A logical security device can be linked with an application from these two objects.
An administrator can be linked with an application from an application object.
A security measure can be linked to an application from the "Assign a security measure" button.
This button is present in the GDPR view and visible in the list of Security controls objects.
In the app, a container can be linked with an application from these two objects.
In the app, the major events field is managed in a separate table.
Major events
Major events are the main events undergone by an application during its operation.
Major events are only accessible through application objects.
They are neither importable nor exportable through the graphics tool.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| m_application_events | N/A |
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| user_id | int unsigned | Mercator user id who has register the event |
| m_application_id | varchar(255) | Reference to the id of the application that suffered the event |
| message | longtext | Description of the event |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
Applications services
An application service is a specific service provided to a user to perform specific tasks related to their role in the organisation.
Eg. an application service could be a Cloud service or platform.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| application_services | /api/application-services |
| Champ | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | Name of the application service |
| description | longtext | Description of the application service |
| exposition | varchar(255) | Exposure of the application service |
| modules | List int [,] | IDs list of related application modules |
| applications | List int [,] | IDs list of related application |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
The data model export lists the applications and application modules linked with an application service.
In the app, an application can be linked with an application service from these two objects.
In the app, an application module can be linked with an application service from these two objects.
There are two fields containing the same information in the data model export, servicesApplications and
applications.
The connection with application objects is made through the applications field.
Application modules
An application module is a component of an application characterized by functional coherence and technological homogeneity.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| application_modules | /api/application-modules |
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | Name of the application module |
| description | longtext | Description of the application module |
| application_services | List int [,] | IDs list of related applications-services |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
The export of the data model lists application services linked with an application module.
In the app, an application service can be linked to an application module from these two objects.
Databases
A database is a set of structured and ordered information meant for computed processing.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| databases | /api/databases |
| Champ | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | Name of the database |
| description | longtext | Description of the database |
| type | varchar(255) | Technology used |
| entity_resp_id | int unsigned | Entity responsible |
| responsible | varchar(255) | Responsible entity |
| icon_id | int unsigned | Reference to a specific icon |
| security_need_c | int | Confidentiality |
| security_need_i | int | Integrity |
| security_need_a | int | Availability |
| security_need_t | int | Traceability |
| security_need_auth | int | Authenticity |
| external | varchar(255) | External |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
In the app, the field for the authenticity need ("security_need_auth") is hidden by default. It is mandatory for
entities subject to the regulation (EU) 2022/2554 (DORA).
This default configuration can be changed in the menu Configuration > Parameters.
The data model export references the specific icon of a database.
In the app, a specific icon can be linked with a database from a database object.
The data model export lists entities using the database (entities field), applications, information, logical servers and containers linked with a database.
In the app, a user entity can be linked with a database from a database object.
In the app, an information can be linked with a database from a database object.
In the app, an application can be linked with a database from these two objects.
In the app, a logical server can be linked with a database from these two objects.
In the app, a container can be linked with a database from these two objects.
Application Flows
An application flow is an exchange of information between a sender and a receiver (application, application service, application module, or database).
An application flow represents an exchange of information between two elements of the information system. It is important to avoid representing all firewall filtering rules in terms of flows.
For example, DNS or NTP requests should not be represented as flows.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| fluxes | /api/fluxes |
| Champ | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | Name of the flow |
| attributes | varchar(255) | Attributs (tags) du flux |
| description | longtext | Description of the flow |
| device_source_id | int unsigned | Link to the source_id |
| device_dest_id | int unsigned | Link to the destination id |
| crypted | tinyint(1) | The flow is encrypted (1=yes, O=no) |
| bidirectional | tinyint(1) | The flow is bidirectional (1=yes, O=no) |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
The device_ for source_id or dest_id can be: :
| Actif (device) | Source | Destination |
|---|---|---|
| Application | ✅ | ✅ |
| Application service | ✅ | ✅ |
| Application module | ✅ | ✅ |
| Database | ✅ | ✅ |
In the app, an information can be linked with an application flow from an application flow object.
Administration areas
Nota: OVI is coming from the French military programme law. The closest equivalents in EU regulations are OES (Operators of Essential Services, EU 2016/1148, NIS) and EE (Essential Entities, EU 2022/2555, NIS 2).
Administration area
An administration zone is a set of resources (people, data, equipment) under the responsibility of one (or more) administrator(s).
An administration zone is made up of Active Directory (AD) directory services and forests, or LDAP trees.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| zone_admins | /api/zone-admins |
| Champ | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | Name of the area |
| description | longtext | Description area |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
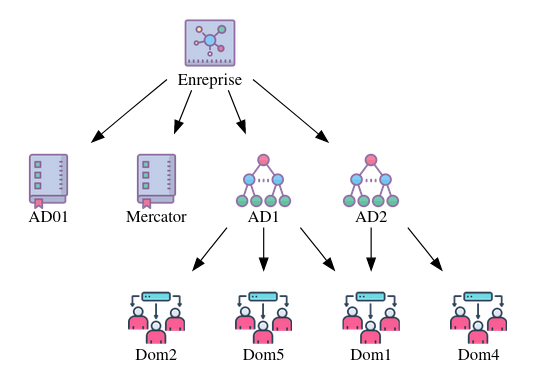
Administration directory services
An administration directory service is an application that collects data on a company's users or IT equipment, enabling them to be administered.
It can be an inventory tool used to manage changes or tickets, or a mapping tool such as Mercator.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| annuaires | /api/annuaires |
| Champ | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | Name of the directory |
| description | longtext | Description of the directory |
| solution | varchar(255) | Techinical solution |
| zone_admin_id | int unsigned | Reference to administration area |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
Active Directory forests / LDAP tree structure
These objects represent an organized grouping of Active Directory domains or LDAP trees.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| forest_ads | /api/forest-ads |
| Champ | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | Name of Active Directory or LDAP forests |
| description | longtext | Description of Active Directory or LDAP forests |
| zone_admin_id | int unsigned | Reference to Administration zone |
| domaines | List int [,] | IDs list of related active directory domaines |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
Active Directory domains / LDAP
Active Directory domains / LDAP are company IT directories. They contains user and computer accounts, contacts, objects rights, and a part of IT policies (e.g. Group Policy Object - GPO).
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| domaine_ads | /api/domaine-ads |
| Champ | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | AD Domain / LDAP name |
| description | longtext | Domain description |
| domain_ctrl_cnt | int signed | Number of domain controllers |
| user_count | int signed | Number of domain users |
| machine_count | int signed | Number of domain computers |
| relation_inter_domaine | varchar(255) | Cross domains relationships description |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
The data model esport lists AD forests / LDAP trees linked with an AD domain / LDAP.
In the app, an AD forest / LDAP tree can be linked with an AD domain / LDAP from these two objects.
A logical server can be linked with an AD domain / LDAP from these two objects.
Users
Users are user accounts with privileged rights on IT systems.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| admin_users | /api/admin-users |
| Champ | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| user_id | varchar(255) | ID number / other of an user |
| firstname | varchar(255) | User's first name |
| lastname | varchar(255) | User's last name |
| type | varchar(255) | User type |
| attributes | varchar(255) | User's tags |
| icon_id | int unsigned | Link to a specific icon |
| description | longtext | User description |
| domain_id | int unsigned | Link to the users's domain |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
The data model export lists applications which an user is administrator.
In the app, an user can be defined as administrator of an application from an application object.
Logical infrastructure
The logical infrastructure view corresponds to the logical distribution of the network.
It illustrates the partitioning of networks and the logical links between them. It also lists the network equipment that handles the traffic.
Networks
Networks are a set of logically interconnected devices that exchange information.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| networks | /api/networks |
| Champ | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | Name of network |
| description | longtext | Description of the network |
| protocol_type | varchar(255) | Used protocols |
| responsible | varchar(255) | Operation manager |
| responsible_sec | varchar(255) | Security manager |
| security_need_c | int | Confidentiality |
| security_need_i | int | Integrity |
| security_need_a | int | Availability |
| security_need_t | int | Traceability |
| security_need_auth | int | Authenticity |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
In the app, the field for the authenticity need ("security_need_auth") is hidden by default. It is mandatory for
entities subject to the regulation (EU) 2022/2554 (DORA).
This default configuration can be changed in the menu Configuration > Parameters.
Subnetworks
Subnetworks are a logical subdivision of a larger network.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| subnetworks | /api/subnetworks |
| Champ | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | Name of the subnet |
| description | longtext | Description of the subnet |
| network_id | int unsigned | ID related to parent network |
| subnetwork_id | int unsigned | ID related to child network |
| connected_subnets_id | int unsigned | Network to which this subnet belongs |
| address | varchar(255) | Addresses range |
| default_gateway | varchar(255) | Default gateway |
| gateway_id | int unsigned | Link to the gateway |
| vlan_id | int unsigned | Associated VLAN |
| ip_allocation_type | varchar(255) | Type of IP address allocation |
| zone | varchar(255) | Name of the firewall zone |
| dmz | varchar(255) | DMZ (Yes/No) |
| wifi | varchar(255) | Wireless (Yes / No) |
| responsible_exp | varchar(255) | Operations manager |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
The field "connected_subnets_id" is a foreign key. However, this one doesn't seem to be used.
External input gateways
Gateways are components used to connect a local network to the outside world.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| gateways | /api/gateways |
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | Name of the gateway |
| description | longtext | Description of the gateway |
| ip | varchar(255) | IP address of the gateway |
| authentification | varchar(255) | Authentication modes |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
In the application, a subnet can be linked with a gateway from these two objects.
Connected external entities
Connected external entities represent external entities connected to the network.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| external_connected_entities | /api/external-connected-entities |
| Champ | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | Name of entity/company |
| type | varchar(255) | Connexion type |
| description | longtext | Description of the entity/company and connection reason |
| entity_id | int unsigned | Reference to the entity (ecosystem view) |
| network_id | int unsigned | Reference to the internal network(s) connected to the entity |
| contacts | varchar(255) | Contacts within the external entity/company |
| src | varchar(255) | Source IP address(es) or source range of the connection |
| src_desc | varchar(255) | Description of the source's connection |
| dst | varchar(255) | Destination IP address(es) or destination range of the connection |
| dst_desc | varchar(255) | Description of the destination's connection |
| security | text | Security requirements of the system |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
The data model export lists subnets and documents attached to a connected external entity.
In the app, a subnet can be linked to a connected external entity from a connected external entity object. A document can be attached to a connected external entity from a connected external entity object.
Network switches
Network switches are the components that manage connections between the various servers on a network.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| network_switches | /api/network-switches |
| Champ | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | Name of the switch |
| description | longtext | Description of the switch |
| ip | varchar(255) | IP address of the switch |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
The data model export lists physical switches and VLANs linked with a network switch.
In the app, a VLAN can be linked with a network switch from these two objects.
A physical switch can be linked with a network switch from these two objects.
Logical routers
Logical routers are logical components that manage connections between different networks.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| routers | /api/routers |
| Champ | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | Name of the router |
| type | varchar(255) | router type |
| ip_addresses | text | IP address(es) of the router |
| description | longtext | Description of the router |
| rules | longtext | Filtering rules |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
The data model export lists physical routers linked to a logical router.
In the app, a physical router can be linked to a logical router from these two objects.
Security devices
Security devices are components used for network supervision, incident detection, equipment protection, and information system security.
Security equipment includes intrusion detection systems (IDS: Intrusion Detection System), intrusion prevention systems (IPS: Intrusion Prevention System) and equipment monitoring systems.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| security_devices | /api/security-devices |
| Champ | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | Name of the device |
| type | varchar(255) | Device type |
| attributes | varchar(255) | Device attributes |
| icon_id | int unsigned | Reference to a specific icon |
| description | longtext | Description of the device |
| address_ip | varchar(255) | IP address(es) of the device |
| vendor | varchar(255) | Vendor / editor for CPE search |
| product | varchar(255) | Editor Product for CPE search |
| version | varchar(255) | Version of a product for CPE search |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
The "vendor", "product" and "version" fields are not used and therefore are absent in the app.
The data model export lists physical security device and applications linked to a logical security device.
In the app, physical security device can be linked to a logical security device from these two objects.
An application can be linked a to logical security device from these two objects.
DHCP servers
***NOTE***: The DHCP servers are kept for backward compatibility and to be compliant with ANSSI's guidelines.
- ANSSI is the French cybersecurity regulation authority.
This object is considered barely usefull and obsolete. It's hidden by default.
DHCP servers are physical or virtual devices that manage a network's IP addresses.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| dhcp_servers | /api/dhcp-servers |
| Champ | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | Name of the DHCP server |
| description | longtext | Description of the DHCP server |
| address_ip | varchar(255) | IP addresse(s) IP of the server |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
DNS servers
***NOTE***: The DNS servers are kept for backward compatibility and to be compliant with ANSSI's guidelines.
- ANSSI is the French cybersecurity regulation authority.
This object is considered barely usefull and obsolete. It's hidden by default.
Domain Name System (DNS) servers are physical or virtual devices that convert a domain name into an IP address.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| dnsservers | /api/dnsservers |
| Champ | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | DNS server's name |
| description | longtext | Description of the DNS server |
| address_ip | varchar(255) | IP address(es) of the server |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
Clusters
Clusters are a set of logical servers hosted on one or more physical servers.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| clusters | /api/clusters |
| Champ | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | Name of the cluster |
| type | varchar(255) | Type of cluster |
| icon_id | int unsigned | Reference to a specific icon |
| description | longtext | Description of the cluster |
| attributes | varchar(255) | Cluster attributes |
| address_ip | varchar(255) | Cluster's IP address |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletionn |
The data model export lists logical routers, logical and physical servers linked with a cluster.
In the app, a logical router can be linked to a cluster from a cluster object.
A logical server can be linked to a cluster from these two objects.
A physical server can be linked to a cluster from these two objects.
Logical servers
Logical servers are a logical breakdown of a physical server. If the physical server is not virtualized, it is split into a single logical server.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| logical_servers | /api/logical-servers |
| Champ | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | Name of the logical server |
| icon_id | int unsigned | Reference to a specific icon |
| type | varchar(255) | Server type (applicative, DB, ...) |
| active | tinyint(1) | Active (1) or obsolete (0) status |
| attributes | varchar(255) | Server attributes (tags) |
| description | longtext | Description of the logical server |
| operating_system | varchar(255) | Operating system |
| install_date | datetime | Date of server installation |
| update_date | datetime | Date of server upgrade |
| patching_frequency | int signed | Recurrence of update |
| next_update | date | Next planned update date |
| net_services | varchar(255) | Active network services |
| environment | varchar(255) | Environnement (prod, dev, test, ...) |
| address_ip | varchar(255) | IP address(es) |
| domain_id | int unsigned | Administration domain for this server |
| cpu | varchar(255) | Number of CPU |
| memory | varchar(255) | Quantity of RAM |
| disk | int | Storage allocated |
| disk_used | int | Storage used |
| configuration | longtext | Server configuration |
| databases | List int [,] | IDs list of related database(s) |
| cluster_id | List int [,] | IDs list of related cluster(s) |
| physical_servers | List int [,] | IDs list of related physical servers |
| applications | List int [,] | IDs list of related applications |
| containers | List int [,] | IDs list of related containers |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
The "patching_frequency" and "next_update" fields are not used and therefore are absent in the app.
The data model lists:
- applications,
- physical servers,
- documents,
- databases,
- clusters,
- certificates,
- and containers
linked with a logical server.
In the app, an application can be linked with a logical server from these two objects.
A database can be linked with a logical server from these two objects.
A cluster can be linked with a logical server from these two objects.
A physical server can be linked with a logical server from these two objects.
A certificate can be linked with a logical server from a certificate object.
A container can be linked with a logical server from a container object.
The "documents" field doesn't appear to be used in a logical server's data model.
Containers
Containers are part of virtualization systems. They can operate in clusters or in isolation. on internal or external (cloud) logical servers.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| containers | /api/containers |
| Champ | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | Container name |
| description | longtext | Container description |
| type | varchar(255) | Type of the container (docker, kubernetes, ...) |
| icon_id | int unsigned | Reference to a specific icon |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
The aata model export lists applications, databases, and logical servers linked with a container.
In the app, an application can be linked to a container from these two objects.
A database can be linked to a container from these two objects.
A logical server can be linked to a container from a container object.
Logical flows
Logical flows describe relationships at layers 3 and 4 of the OSI model.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| logical_flows | /api/logical-flows |
General principle :
| Champ | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | Name of logical flow |
| description | text | Description of logical flow |
| chain | varchar(255) | INPUT / OUTPUT / FORWARD |
| interface | varchar(255) | Network interface used |
| router_id | int unsigned | Router used for this logical flow |
| priority | int signed | Priority of the rule / flow |
| action | varchar(255) | Rule action (Allow, deny, restrict, ...) |
| protocol | varchar(255) | Protocol(s) used by this flow |
| source_ip_range | varchar(255) | Source IP range |
| dest_ip_range | varchar(255) | Destination IP range |
| source_port | varchar(255) | Logical port of the source |
| dest_port | varchar(255) | Logical port of the destination |
| device_source_id | int unsigned | Source device |
| device_dest_id | int unsigned | Destination device |
| users | varchar(255) | Users concerned by this flow rule |
| schedule | varchar(255) | Period of activity of the rule/flow |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
Source and destination devices can be:
| device | Source | Destination |
|---|---|---|
| Peripherals | ✅ | ✅ |
| Physical security device | ✅ | ✅ |
| Physical server | ✅ | ✅ |
| Storage infrastructure | ✅ | ✅ |
| Workstations | ✅ | ✅ |
| Logical security device | ✅ | ✅ |
| Logical server | ✅ | ✅ |
| Subnetworks | ✅ | ✅ |
Certificates
Electronic certificates are used to identify and authenticate services and individuals, as well as to encrypt exchanges.
Certificates are SSL keys, HTTPS certificates, etc. They are associated with logical servers or applications.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| certificates | /api/certificates |
| Champ | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | Name of the certificate |
| description | longtext | Description of the certificate |
| type | varchar(255) | Type of certificate (SSL, HTTPS ...) |
| start_validity | date | Start date of validity |
| end_validity | date | End date of validity |
| status | int | Certificate statis (RFC 6960) |
| last_notification | datetime | Last notification sent |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
- Note:
- status = 0 : "Good"
- status = 1 : "Revoked"
- status = 2 : "Unknown"
The "last_notification" field is not used and therefore is absent in the app.
The data model export lists applications and logical servers linked with a certificate.
In the app, a certificate can be linked to a application or a logical server from a certificate object.
VLANs
A VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) or virtual LAN enables equipment to be logically grouped together, free from physical constraints.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| vlans | /api/vlans |
| Champ | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | Name of VLAN |
| description | longtext | Description of VLAN |
| vlan_id | int signed | VLAN number |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
The data model export lists physical routers and logical network switches linked to a VLAN.
In the app, a VLAN can be linked to a physical router from a physical router object.
In the app, a VLAN can be linked to a subnet from these two objects.
In the app, a VLAN can be linked to a logic switch from these two objects.
Physical infrastructure
The physical infrastructure view describes the physical equipment that makes up or is used by the information system.
This view corresponds to the geographical distribution of network equipment within the various sites.
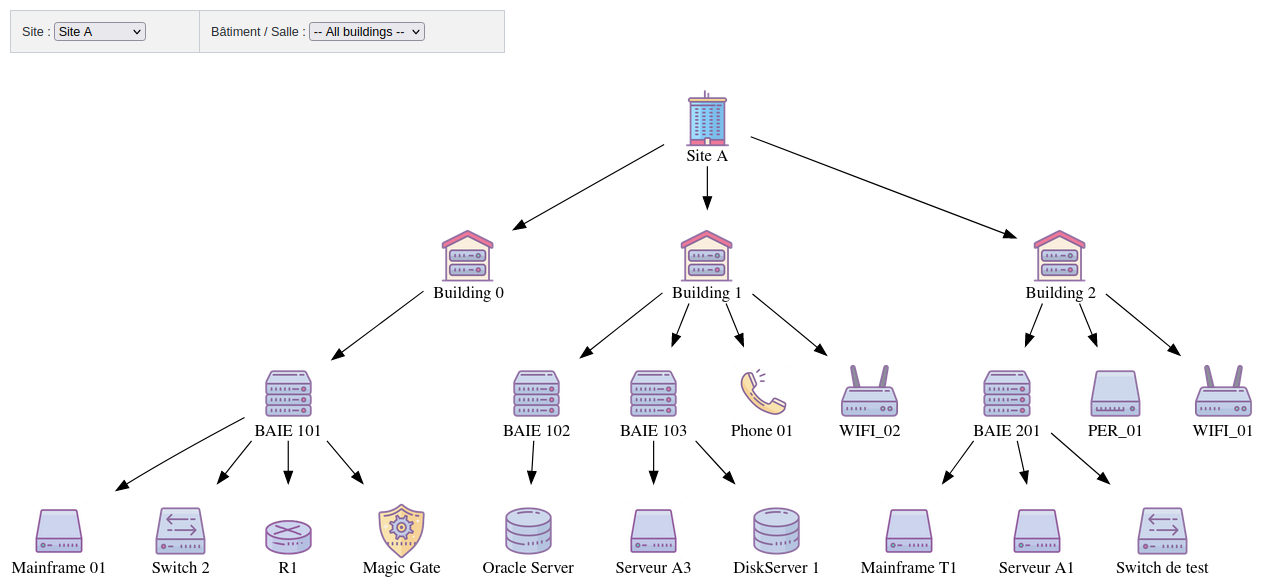
Sites
Sites are geographical locations that bring together a group of people and/or resources.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| sites | /api/sites |
| Champ | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | Name of the site |
| icon_id | int unsigned | Reference to a specific icon |
| description | longtext | Description of the site |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
In the app, a building / room can be linked with a site from a building / room objet.
Buildings / Rooms
Buildings or rooms represent the location of people or resources within a site.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| buildings | /api/buildings |
| Champ | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | Name of building |
| icon_id | int unsigned | Reference to a specific icon |
| type | varchar(255) | Type of Room/Building |
| attributes | varchar(255) | Attributes of the building / room |
| description | longtext | Description of the building |
| site_id | int unsigned | Reference to the site |
| building_id | int unsigned | Reference to a building / room |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
In the app, a building / room or a site can be linked with a building / room from a building object / room.
Racks
Racks are technical cabinets housing computer network or telephony equipment.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| bays | /api/bays |
| Champ | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | Name of the rack |
| description | longtext | Description of the rack |
| room_id | int unsigned | Reference to building / room |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
In the app, a rack can be linked to a building / room from a rack objet.
Physical servers
Physical servers are physical machines running a set of IT services.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| physical_servers | /api/physical-servers |
| Champ | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | Name of physical server |
| icon_id | int unsigned | Reference to a specific icon |
| description | longtext | Description of physical server |
| type | varchar(255) | Type / model of server |
| cpu | varchar(255) | Number of CPU |
| memory | varchar(255) | Quantity of RAM |
| disk | int | Storage allocated |
| disk_used | int | Storage used |
| configuration | longtext | Server configuration |
| operating_system | varchar(255) | Operating system |
| address_ip | varchar(255) | IP address |
| install_date | datetime | Date of server installation |
| update_date | datetime | Date of server upgrade |
| responsible | varchar(255) | Person/Team responsible for the server |
| site_id | int unsigned | Reference to the site |
| building_id | int unsigned | Reference to the building / room |
| bay_id | int unsigned | Reference to the rack |
| clusters | List int [,] | IDs list of related cluster(s) |
| logical_servers | List int [,] | IDs list of related logical(s) servers(s) |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
The data model export lists applications, (logical) clusters, and logical servers linked with a physical server.
In the app, an application can be linked with a physical server from a physical server object.
A cluster can be linked with a physical server from these two types of objects.
A logical server can be linked with a physical server from these two types of objects.
For readability purpose, fields defined in the data model but unused in the app for the table physical_servers have been gathered into the following table:
| Champ | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| vendor | varchar(255) | Vendor / editor for CPE search |
| product | varchar(255) | Product of an editor for CPE search |
| version | varchar(255) | Version of a product for CPE search |
| patching_group | varchar(255) | Group for upgrade |
| patching_frequency | varchar(255) | Frequency of upgrade |
| next_update | date | Date of next upgrade |
| physical_swicth_id | int unsigned | ID of related Physical switch |
Workstations
Workstations are physical machines that enable a user to access the information system.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| workstations | /api/workstations |
| Champ | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | Name of workstation |
| icon_id | int unsigned | Reference to a specific icon |
| description | longtext | Description of workstation |
| status | varchar(255) | Status of the workstation (lifecycle, incidents) |
| type | varchar(255) | Type / model of workstation |
| entity_id | int unsigned | ID of the related entity |
| domain_id | int unsigned | ID of the related users identification domain |
| user_id | int unsigned | User ID if inside the domain (admin view) |
| other_user | int unsigned | Workstation users, if outside of domain |
| manufacturer | varchar(255) | Workstation manufacturer |
| model | varchar(255) | Workstation model |
| serial_number | varchar(255) | Workstation serial number |
| cpu | varchar(255) | Workstation CPU |
| memory | varchar(255) | Workstation RAM |
| disk | int signed | Disk size of the workstation |
| operating_system | varchar(255) | Operating system |
| network_id | int unsigned | ID of the related network |
| address_ip | varchar(255) | IP address(es) of the workstation |
| mac_address | varchar(255) | MAC address(es) of the workstation |
| network_port_type | varchar(255) | Network connector type (RJ45, USB, SFP,...) |
| site_id | int unsigned | Reference to site |
| building_id | int unsigned | Reference to building / room |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
The data model export lists applications linked to a workstation.
In the app, an application can be linked to a workstation from a workstation object.
For readability purpose, fields defined in the data model but unused in the app for the table workstations have been gathered in the following table:
| Champ | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| vendor | varchar(255) | Vendor / editor for CPE search |
| product | varchar(255) | Product of an editor for CPE search |
| version | varchar(255) | Version of a product for CPE search |
| warranty | varchar(255) | Guarantee contract |
| warranty_start_date | date | Guarantee start date |
| warranty_end_date | date | Guarantee end date |
| warranty_period | date | Guarantee period |
| purchase_date | date | Purchase date |
| fin_value | decimal | Financial value. |
| last_inventory_date | date | Date of last inventory |
| update_source | varchar(255) | Source of inventory update |
| agent_version | varchar(255) | Inventory agent version |
| physical_swicth_id | int unsigned | ID related to the physical switch |
The "vendor", "product" and "version" fields are not used and therefore are absent of the app.
Storage infrastructures
***NOTE***: The storage infrastructures are kept for compatibility, but this table is not maintained anymore.
It is possible to replace this asset by:
- A logical server.
- A physical server.
Storage infrastructures are physical media or data storage networks: network attached storage (NAS), storage area network (SAN), hard disk...
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| storage_devices | /api/storage-devices |
| Champ | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | Name of storage infrastructure |
| type | varchar(255) | Storage infrastructure type (NAS, SAN, HDD, etc.) |
| description | longtext | Description of the storage infrastructure |
| site_id | int unsigned | Reference to the site |
| building_id | int unsigned | Reference to building / room |
| bay_id | int unsigned | Reference to the rack |
| address_ip | varchar(255) | IP address of storage infrastructure |
| vendor | varchar(255) | Vendor / editor for CPE search |
| product | varchar(255) | Product of an editor for CPE search |
| version | varchar(255) | Version of a product for CPE search |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
The "vendor", "product" and "version" fields are not used and therefore are absent of the app.
Peripherals
Peripherals are physical components connected to a workstation to add new functions (e.g. keyboard, mouse, printer, scanner, etc.).
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| peripherals | /api/peripherals |
| Champ | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | Name of peripheral |
| description | longtext | Description of peripheral |
| type | varchar(255) | Type / model of peripheral |
| icon_id | int unsigned | Reference to a specific icon |
| site_id | int unsigned | Reference to site |
| building_id | int unsigned | Reference to building / room |
| bay_id | int unsigned | Reference to rack |
| responsible | varchar(255) | Internal responsible of this peripheral |
| address_ip | varchar(255) | IP address of the peripheral |
| domain | varchar(255) | General domain where it fits to (IT, OT, IOT, etc.) |
| vendor | varchar(255) | Vendor / editor for CPE search |
| product | varchar(255) | Product of an editor for CPE search |
| version | varchar(255) | Version of a product for CPE search |
| provider_id | int unsigned | ID related to the provider of this peripheral |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
The data model export lists applications using a peripheral.
In the app, an application can be linked to a peripheral from a peripheral object.
Phones
Landlines and mobile phones belonging to the organization.
| Champ | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | Name of telephone |
| description | longtext | Description of telephone |
| type | varchar(255) | Type / model of telephone |
| vendor | varchar(255) | Vendor / editor for CPE search |
| product | varchar(255) | Product of an editor for CPE search |
| version | varchar(255) | Version of a product for CPE search |
| site_id | int unsigned | Reference to site |
| building_id | int unsigned | Reference to building / room |
| physical_switch_id | int unsigned | ID related to the physical switch |
| address_ip | varchar(255) | IP address of the phone |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
The "vendor", "product" and "version" fields are not used and therefore are absent in the app.
The filed "physical_switch_id" is not used and therefore is absent in the app. However, a phone object can be linked with a network switch (either physical or logical) through a physical link object.
Physical switches
Physical switches are physical components that manage connections between different servers within a network.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| physical_switches | /api/physical-switches |
| Champ | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | Name of physical switch |
| description | longtext | Description of physical switch |
| type | varchar(255) | Type / model of physical switch |
| site_id | int unsigned | Reference to site |
| building_id | int unsigned | Reference to building / room |
| bay_id | int unsigned | Reference to rack |
| vendor | varchar(255) | Vendor / editor for CPE search |
| product | varchar(255) | Product of an editor for CPE search |
| version | varchar(255) | Version of a product for CPE search |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
The "vendor", "product" and "version" fields are not used and therefore are absent in the app.
The data model export lists logical network switches linked with a physical switch.
In the app, a physical switch can be linked with a logical network switch from these two objects.
Physical routers
Physical routers are physical components that manage connections between different networks.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| physical_routers | /api/physical_routers |
| Champ | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | Name of physical router |
| description | longtext | Description of physical router |
| type | varchar(255) | Type / model of physical router |
| site_id | int unsigned | Reference to site |
| building_id | int unsigned | Reference to building / room |
| bay_id | int unsigned | Reference to rack |
| vendor | varchar(255) | Vendor / editor for CPE search |
| product | varchar(255) | Product of an editor for CPE search |
| version | varchar(255) | Version of a product for CPE search |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
The "vendor", "product" and "version" fields are not used and therefore are absent in the app.
The data model export lists logical routers and VLANs linked to a physical router.
In the app, a physical router can be linked to a logical router (denoted as "Routers") from these two types of
objects.
A VLAN can be linked to a physical router from a physical router object.
WiFi terminals
WiFi hotspots are hardware devices that enable access to the WiFi wireless network.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| wifi_terminals | /api/wifi-terminals |
| Champ | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | Name of WiFi hotspot |
| description | longtext | Description of WiFi hotspot |
| type | varchar(255) | Type / model of WiFi hotspot |
| site_id | int unsigned | Reference to site |
| building_id | int unsigned | Reference to building / room |
| address_ip | varchar(255) | IP address of the wifi terminal |
| vendor | varchar(255) | Vendor / editor for CPE search |
| product | varchar(255) | Product of an editor for CPE search |
| version | varchar(255) | Version of a product for CPE search |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
Physical security device
Physical security device includes components for network supervision, incident detection, equipment protection, and information system security.
Physical security device includes temperature sensors, cameras, security doors, etc.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| physical_security_devices | /api/physical-security-devices |
| Champ | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | Name of security device |
| icon_id | int unsigned | Reference to a specific icon |
| description | longtext | Description of security device |
| type | varchar(255) | Type / model of security device |
| site_id | int unsigned | Reference to site |
| building_id | int unsigned | Reference to building / room |
| bay_id | int unsigned | Reference to rack |
| address_ip | varchar(255) | IP sddress |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
The data model export lists logical security devices linked to a physical security device.
In the app, a logical security device can be linked to a physical security device from these two objects.
Physical links
Physical links represent the cables between physical or logical objects.
Logical objects can have physical links, for example within a virtualized network.
A physical link is different from a logical flow. A physical link describes a relationship at layers 1 or 2 of the OSI
model.
A logic flow describes a relationship at layers 3 and 4 of the OSI model.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| physical_links | /api/physical-links |
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| device_src_id | int unsigned | Source |
| src_id | varchar(255) | Physical port of the source device |
| device_dst_id | int unsigned | Destination |
| dst_port | varchar(255) | Physical port of the destination device |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
Source and destination devices can be:
| device | Source | Destination |
|---|---|---|
| Peripheral device | ✅ | ✅ |
| Phone | ✅ | ✅ |
| Physical router | ✅ | ✅ |
| Physical security device | ✅ | ✅ |
| Physical server | ✅ | ✅ |
| Physical switch | ✅ | ✅ |
| Storage infrastructure | ✅ | ✅ |
| Wifi terminal | ✅ | ✅ |
| Workstation | ✅ | ✅ |
| Logical server | ✅ | ✅ |
| Logical switch | ✅ | ✅ |
| Logical router | ✅ | ✅ |
WANs
WANs (Wide Area Networks) are computer networks linking equipment over long distances. They generally interconnect MANs or LANs.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| wans | /api/wans |
| Champ | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | Name of WAN |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
The data model export lists LANs and MANs linked to a WAN.
In the app, a LAN can be linked to a WAN from a WAN object.
A MAN can be linked to a WAN from a WAN object.
MANs
MANs (Middle Area Networks) are computer networks linking equipment over medium-sized distances. They generally interconnect LANs.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| mans | /api/mans |
| Champ | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | Name of MAN |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
The data model export lists WANs and LANs linked to a MAN.
In the app, a WAN can be linked to a MAN from a WAN object.
A LAN can be linked to a MAN from a MAN object.
LANs
LANs (Local Area Networks) are computer networks linking equipment over a small geographical area.
| Table | api |
|---|---|
| lans | /api/lans |
| Champ | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | int unsigned | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(255) | Name of LAN |
| description | longtext | Description of LAN |
| created_at | timestamp | Date of creation |
| updated_at | timestamp | Date of update |
| deleted_at | timestamp | Date of deletion |
The data model export lists MANs and WANs linked to a LAN.
In the app, a MAN can be linked to a LAN from a MAN object.
A WAN can be linked to a LAN from a WAN object.